Important Safety Information
Infections: Fatal and serious infections (including bacterial, viral, fungal) and opportunistic infections occurred in Jaypirca-treated patients. In a clinical trial, Grade ≥3 infections occurred in 24% of patients with hematologic malignancies, most commonly pneumonia (14%); fatal infections occurred in 4.4%. Sepsis (6%) and febrile neutropenia (4%) occurred. In patients with CLL/SLL, Grade ≥3 infections occurred (32%), with fatal infections occurring in 8%. Opportunistic infections included Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and fungal infection. Consider prophylaxis, including vaccinations and antimicrobial prophylaxis, in patients at increased risk for infection, including opportunistic infections. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms, evaluate promptly, and treat appropriately. Based on severity, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue Jaypirca.
Hemorrhage: Fatal and serious hemorrhage has occurred with Jaypirca. Major hemorrhage (Grade ≥3 bleeding or any central nervous system bleeding) occurred in 3% of patients, including gastrointestinal hemorrhage; fatal hemorrhage occurred (0.3%). Bleeding of any grade, excluding bruising and petechiae, occurred in 17%. Major hemorrhage occurred in patients taking Jaypirca with (0.7%) and without (2.3%) antithrombotic agents. Consider risks/benefits of co-administering antithrombotic agents with Jaypirca. Monitor patients for signs of bleeding. Based on severity, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue Jaypirca. Consider benefit/risk of withholding Jaypirca 3-7 days pre- and post-surgery depending on type of surgery and bleeding risk.
Cytopenias: Jaypirca can cause cytopenias, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. In a clinical trial, Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias, including decreased neutrophils (26%), decreased platelets (12%), and decreased hemoglobin (12%), developed in Jaypirca-treated patients. Grade 4 decreased neutrophils (14%) and Grade 4 decreased platelets (6%) developed. Monitor complete blood counts regularly during treatment. Based on severity, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue Jaypirca.
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Cardiac arrhythmias occurred in patients who received Jaypirca. In a clinical trial of patients with hematologic malignancies, atrial fibrillation or flutter were reported in 3.2% of Jaypirca-treated patients, with Grade 3 or 4 atrial fibrillation or flutter in 1.5%. Other serious cardiac arrhythmias such as supraventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest occurred (0.5%). Patients with cardiac risk factors such as hypertension or previous arrhythmias may be at increased risk. Monitor for signs and symptoms of arrhythmias (e.g., palpitations, dizziness, syncope, dyspnea) and manage appropriately. Based on severity, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue Jaypirca.
Second Primary Malignancies: Second primary malignancies, including non-skin carcinomas, developed in 9% of Jaypirca-treated patients. The most frequent malignancy was non-melanoma skin cancer (4.6%). Other second primary malignancies included solid tumors (including genitourinary and breast cancers) and melanoma. Advise patients to use sun protection and monitor for development of second primary malignancies.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Jaypirca can cause fetal harm in pregnant women. Administration of pirtobrutinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused embryo-fetal toxicity, including embryo-fetal mortality and malformations at maternal exposures (AUC) approximately 3-times the recommended 200 mg/day dose. Advise pregnant women of potential fetal risk and females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for one week after last dose.
Adverse Reactions (ARs) in Patients Who Received Jaypirca
The most common (≥20%) ARs in the BRUIN pooled safety population of patients with hematologic malignancies (n=593) were decreased neutrophil count (46%), decreased hemoglobin (39%), fatigue (32%), decreased lymphocyte count (31%), musculoskeletal pain (30%), decreased platelet count (29%), diarrhea (24%), COVID-19 (22%), bruising (21%), cough (20%).
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Serious ARs occurred in 38% of patients. Serious ARs occurring in ≥2% of patients were pneumonia (14%), COVID-19 (4.7%), musculoskeletal pain (3.9%), hemorrhage (2.3%), pleural effusion (2.3%), and sepsis (2.3%). Fatal ARs within 28 days of last Jaypirca dose occurred in 7% of patients, most commonly due to infections (4.7%), including COVID-19 (3.1% of all patients).
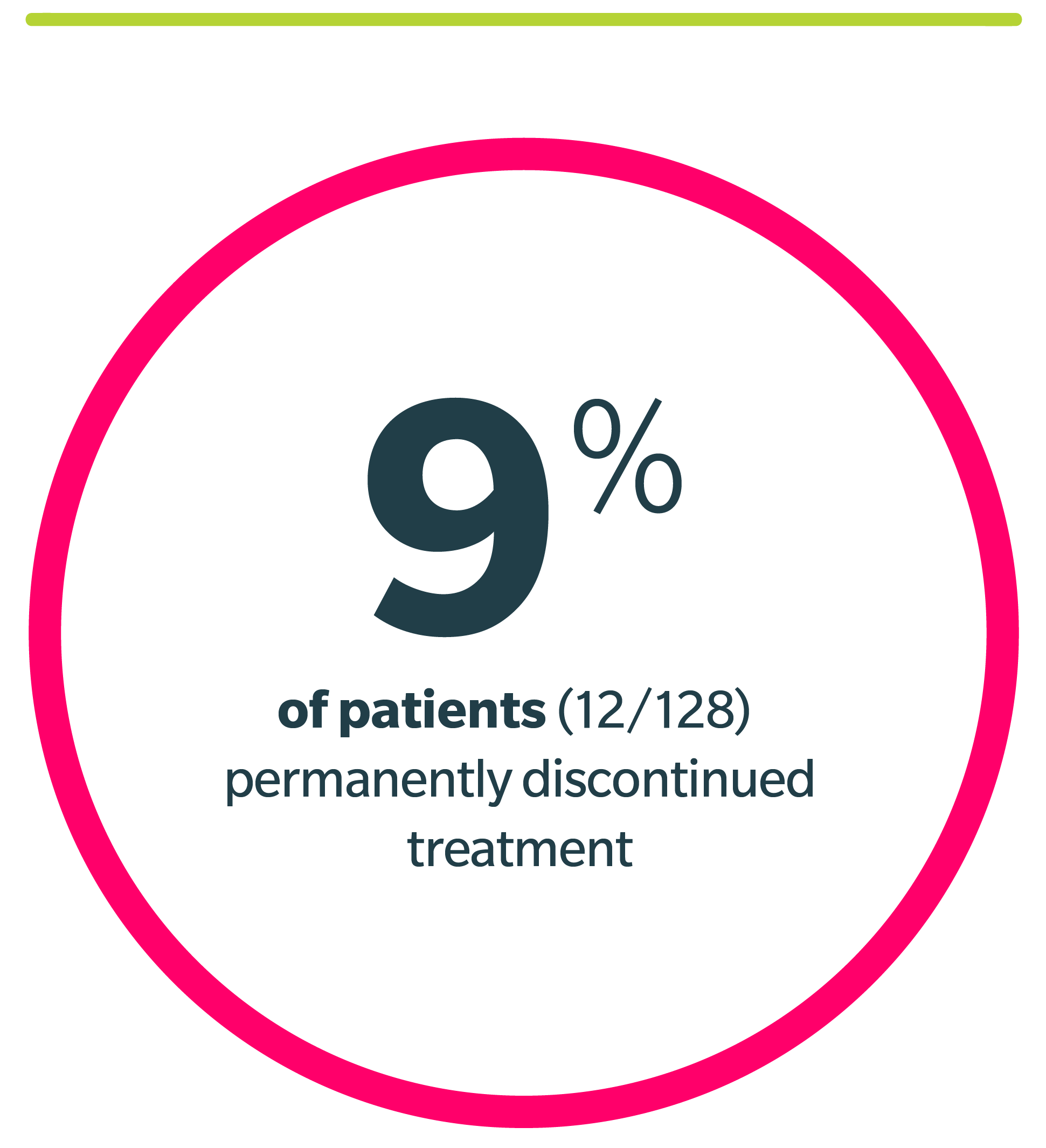
Dose Modifications and Discontinuations: ARs led to dose reductions in 4.7%, treatment interruption in 32%, and permanent discontinuation of Jaypirca in 9% of patients. ARs resulting in dosage modification in >5% of patients included pneumonia and neutropenia. ARs resulting in permanent discontinuation in >1% of patients included pneumonia.
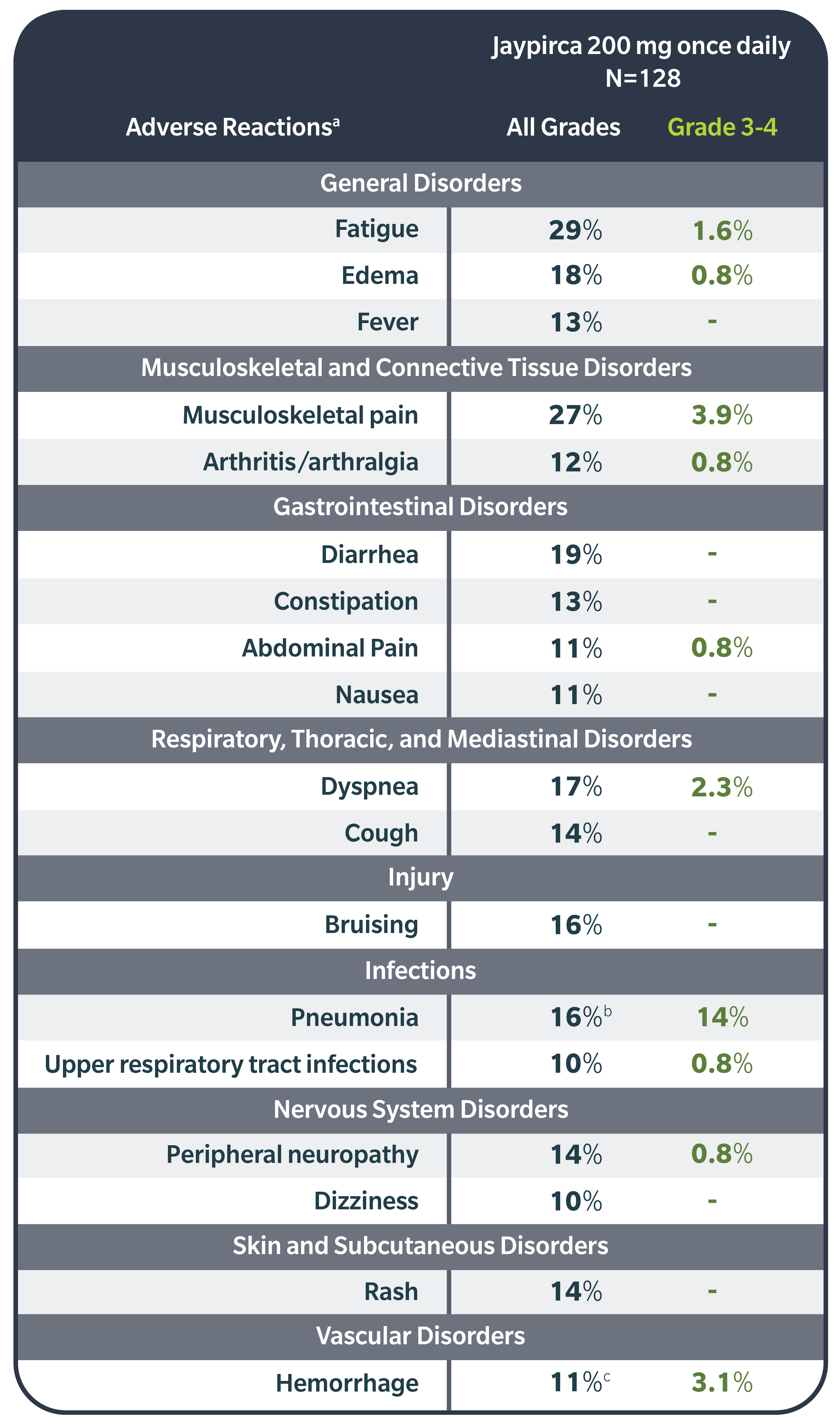
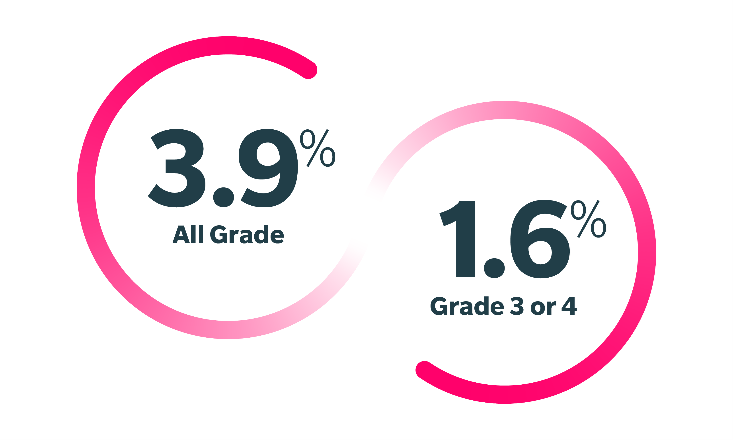
ARs (all Grades %; Grade 3-4 %) in ≥10% of Patients: fatigue (29; 1.6), musculoskeletal pain (27; 3.9), diarrhea (19; -), edema (18; 0.8), dyspnea (17; 2.3), pneumonia (16; 14), bruising (16; -), peripheral neuropathy (14; 0.8), cough (14; -), rash (14; -), fever (13; -), constipation (13; -), arthritis/arthralgia (12; 0.8), hemorrhage (11; 3.1), abdominal pain (11; 0.8), nausea (11; -), upper respiratory tract infections (10; 0.8), dizziness (10; -).
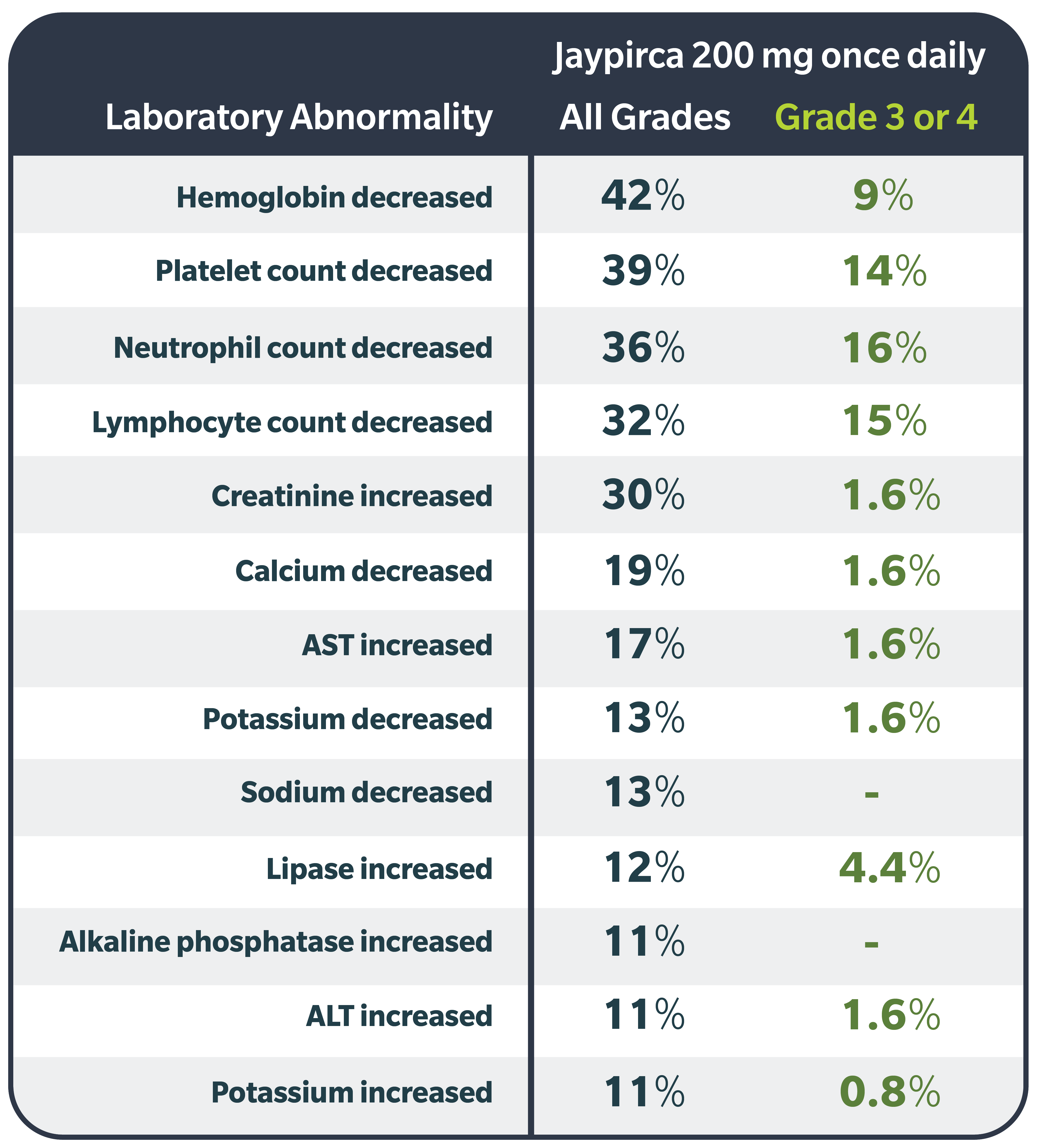
Select Laboratory Abnormalities (all Grades %; Grade 3 or 4 %) that Worsened from Baseline in ≥10% of Patients: hemoglobin decreased (42; 9), platelet count decreased (39; 14), neutrophil count decreased (36; 16), lymphocyte count decreased (32; 15), creatinine increased (30; 1.6), calcium decreased (19; 1.6), AST increased (17; 1.6), potassium decreased (13; 1.6), sodium decreased (13; -), lipase increased (12; 4.4), alkaline phosphatase increased (11; -), ALT increased (11; 1.6), potassium increased (11; 0.8). Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in >5% of patients included neutrophils decreased (10), platelets decreased (7), lymphocytes decreased (6).
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
Serious ARs occurred in 56% of patients. Serious ARs occurring in ≥5% of patients were pneumonia (18%), COVID-19 (9%), sepsis (7%), and febrile neutropenia (7%). Fatal ARs within 28 days of last Jaypirca dose occurred in 11% of patients, most commonly due to infections (10%), including sepsis (5%) and COVID-19 (2.7%).
Dose Modifications and Discontinuations: ARs led to dose reductions in 3.6%, treatment interruption in 42%, and permanent discontinuation of Jaypirca in 9% of patients. ARs resulting in dose reductions in >1% included neutropenia; treatment interruptions in >5% of patients included pneumonia, neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and COVID-19; permanent discontinuation in >1% of patients included second primary malignancy, COVID-19, and sepsis.
ARs (all Grades %; Grade 3-4 %) in ≥10% of Patients: fatigue (36; 2.7), bruising (36; -), cough (33; -), musculoskeletal pain (32; 0.9), COVID-19 (28; 7), pneumonia (27; 16), diarrhea (26; -), abdominal pain (25; 2.7), dyspnea (22; 2.7), hemorrhage (22; 2.7), edema (21; -), nausea (21; -), pyrexia (20; 2.7), headache (20; 0.9), arthritis/arthralgia (19; 1.8), rash (19; 0.9), peripheral neuropathy (16; 3.6), dizziness (15; -), fall (14; 0.9), constipation (14; -), insomnia (14; -), upper respiratory tract infections (13; 2.7), second primary malignancy (13; 2.7), renal insufficiency (12; 6), hypertension (12; 5), neurological changes (12; 2.7), mucositis (12; 0.9), decreased appetite (12; -), respiratory tract infection (11; 1.8), supraventricular tachycardia (10; 5).
Select Laboratory Abnormalities (all Grades %; Grade 3 or 4 %) that Worsened from Baseline in ≥20% of Patients: neutrophil count decreased (63; 45), hemoglobin decreased (48; 19), calcium decreased (40; 2.8), platelet count decreased (30; 15), sodium decreased (30; -), lymphocyte count decreased (23; 8), ALT increased (23; 2.8), AST increased (23; 1.9), creatinine increased (23; -), lipase increased (21; 7), alkaline phosphatase increased (21; -). Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in >5% of patients included neutrophils decreased (23).
Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Concomitant use with Jaypirca increased pirtobrutinib systemic exposure, which may increase risk of Jaypirca ARs. Avoid use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with Jaypirca. If concomitant use is unavoidable, reduce Jaypirca dosage according to approved labeling.
Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Concomitant use with Jaypirca decreased pirtobrutinib systemic exposure, which may reduce Jaypirca efficacy. Avoid concomitant use of Jaypirca with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers. If concomitant use with moderate CYP3A inducers is unavoidable, increase Jaypirca dosage according to approved labeling.
Sensitive CYP2C8, CYP2C19, CYP3A, P-gp, or BCRP Substrates: Concomitant use with Jaypirca increased their plasma concentrations, which may increase risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates for drugs that are sensitive to minimal concentration changes. Follow recommendations for these sensitive substrates in their approved labeling.
Use in Special Populations
Pregnancy and Lactation: Due to potential for Jaypirca to cause fetal harm, verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to starting Jaypirca and advise use of effective contraception during treatment and for one week after last dose. Presence of pirtobrutinib in human milk is unknown. Advise women not to breastfeed while taking Jaypirca and for one week after last dose.
Geriatric Use: In the pooled safety population of patients with hematologic malignancies, patients aged ≥65 years experienced higher rates of Grade ≥3 ARs and serious ARs compared to patients <65 years of age.
Renal Impairment: Severe renal impairment increases pirtobrutinib exposure. Reduce Jaypirca dosage in patients with severe renal impairment according to approved labeling.
PT HCP ISI COMBO DEC2023
Please see full Prescribing Information and Patient Information for Jaypirca.